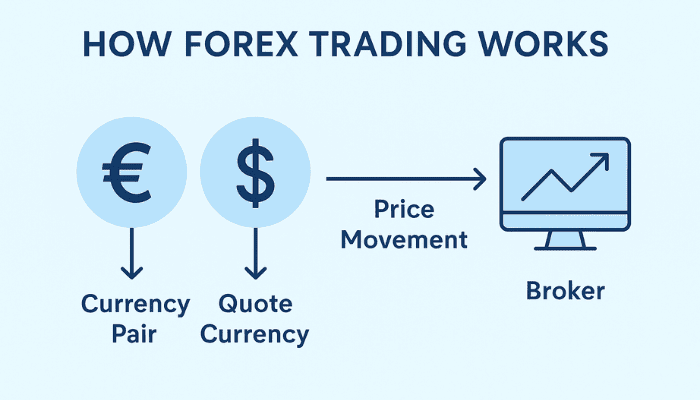
Forex trading works by buying one currency while selling another at the same time. You can trade currency pairs, like EUR/USD or GBP/JPY, and the exchange rate tells you how much one currency is worth compared to the other.
When you trade Forex, you’re not exchanging physical money. Instead, you’re speculating on whether the price of one currency will go up or down compared to another.
Key Concepts:
- Currency Pairs
- Each trade involves two currencies.
- The base currency is the first one (e.g., EUR in EUR/USD).
- The quote currency is the second one (e.g., USD in EUR/USD).
- Exchange Rate
- This shows how much of the quote currency you need to buy one unit of the base currency.
- For example, if EUR/USD = 1.10, it means 1 Euro costs 1.10 US Dollars.
- Buying and Selling
- If you think the base currency will strengthen (increase in value), you buy the pair.
- If you think it will get weaker (go down), you sell the pair.
- Profit and Loss
- You make money if the exchange rate moves in your favor after you open the trade.
- If it moves against you, you lose money.
- Bid and Ask Prices (The Spread)
- The bid price is the price at which you sell the currency pair.
- The ask price is the price at which you buy the currency pair.
- The difference between them is called the spread, which is a small cost when you trade.
- How Trades are Executed
- You use a Forex broker who provides a trading platform.
- You place orders to buy or sell currency pairs through the broker.
- Market Hours
- The Forex market is open 24 hours a day, 5 days a week.
- It moves through different sessions (London, New York, Tokyo) where volume and activity change.